1-(a)គណនា
(b)កំនត់ f(0) ដើម្បីអោយអនុគមន័ខាងក្រោមជាប់ត្រង់ x=0 :
2-(a)រកបរមា និងអាស៊ីមតូតរបស់អនុគមន៍ y=x+arccotg2x.
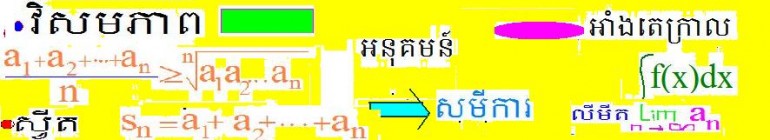
(b)បង្ហាញវិសមភាព ផ្ទៀងផ្ទាត់គ្រប់x.
3-គណនាអាំងតេក្រាលខាងក្រោម:
(a)
(b)
4-គេអោយអនុគមន៍ប៉ារ៉ាម៉ែត :
(a)គណនា
(b)គណនាប្រវែងកំនោងពេល t ប្រែប្រួលពី
6-កំនត់អនុគមន៍h(x) ដែល ជាឌីផេរ៉ង់ស្យែលគ្រប់នៃអនុគមន៍f(x,y).
-គណនា f(x,y) បើ f(1,0)=1;